
That the higher the degrees, the more open this angle is. And then as we goįurther and further up, I guess, since this That- so you don't always have to do it inĬenter of the protractor at the vertex of the angle. So that the angle is still within the protractor. You want to rotate the 0 degrees to one of the sides So that the 0 degrees is- and what you want to do is The angle right over here, if we look at where the So that this angle will be within the protractor. And let's get thisĠ degrees side to be on one of these sides So once again, let us put theĬenter of the protractor right at the vertex right over there. It would have beenĮmbarrassing if I didn't. Need to measure here is 130 degrees, assuming Look at it this way, you can see that the angle- and This edge right over here is right along this line.

This edge at 0 degrees, is at one of these sides. To rotate it so that, preferably, this edge, Of the protractor right at the vertex of where Measure any angle using an actual physical protractor. Would actually measure it the way you would Use this protractor to measure the angles there. And he made this reallyĬool protractor tool here so that you actually One of our amazing high school interns that we had Time that I'm doing this video, there is no video for the The measuring angles module because, clearly, at the There are a variety of other terms for various kinds of pairings of angles. Vertical angles: the angles on opposite sides of two intersecting lines In other words, one of the outside four angles a transversal creates.Īdjacent angles: two angles which share one common side and share a common vertex. Interior angle (meaning two): any of the four angles formed between two lines where a transversal intersects them.Įxterior angle (meaning one): an angle on the outside of a polygon formed by a side and its extended adjacent side.Įxterior angle (meaning two): any of the four angles formed by a transversal that are not between the two lines the transversal intersects. Interior angle (meaning one): the angle inside of a polygon formed by the meeting of two sides. Supplementary angles: two angles that add up to 180°Įxplementary or conjugate angles: two angles that add up to 360°. Oblique angle: any angle other than 0° or a multiple of 90°Ĭomplementary angles: two angles that add up to 90°
To be able to establish the measure of an angle by using its complementary (example of the javelin and of the inclined road).There are countless special names for angles, but many of these are not important at this level of study.
ANGLES PROTRACTOR HOW TO
To teach how to place a protractor in order to properly measure an angle.
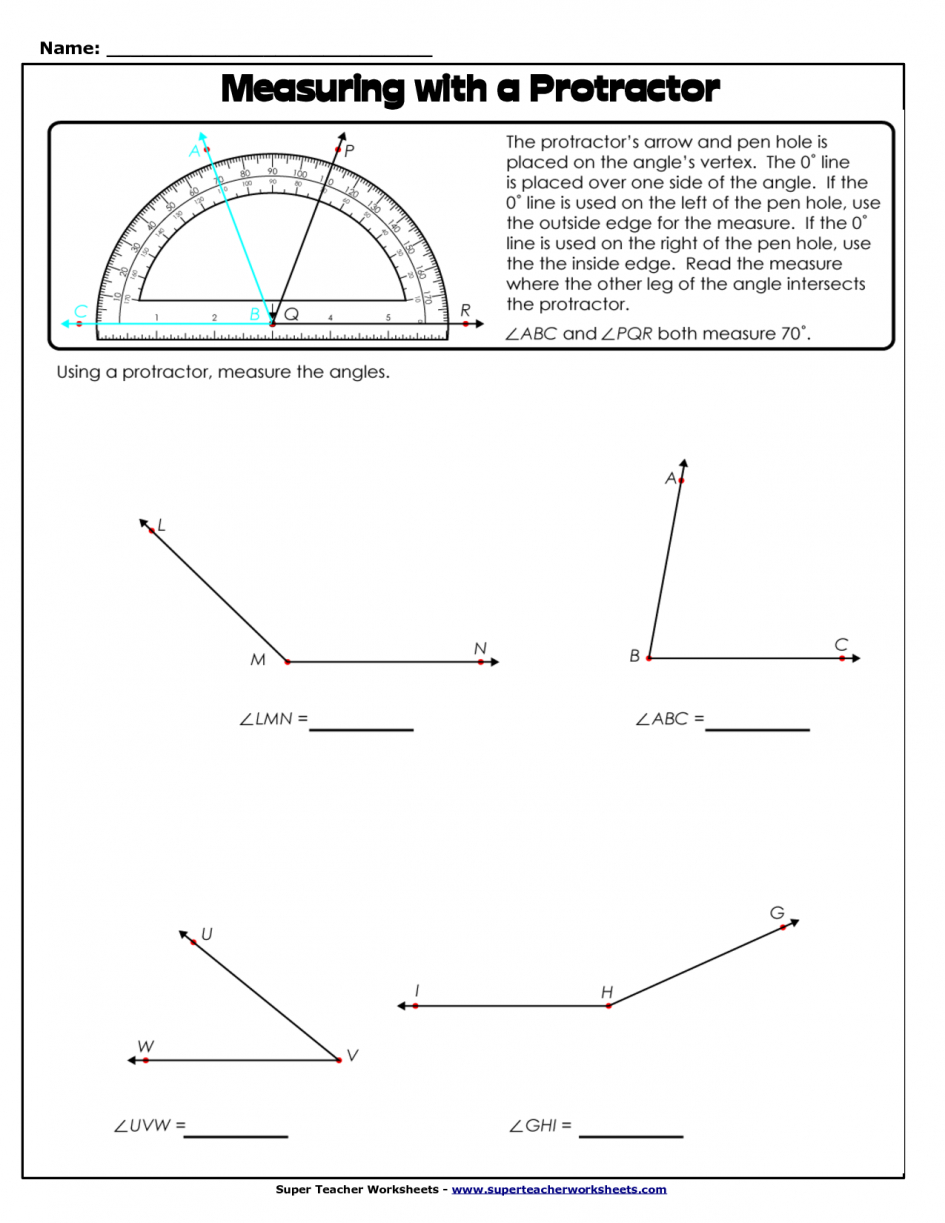

Position the origin of the protractor on the tip of the angle to measure.The most common units of measures for angles are the degree (°) and the radian (rad). To facilitate its usage, the protractor often possesses two graduations going in both directions.
ANGLES PROTRACTOR FULL
Another form of protractors available would be the full disc graduated from 0 to 360°. The protractor is graduated from 0 to 180 degrees (°). The most popular version is the half disc split into 180 equal parts that each correspond to one degree. The tool used to measure angles is the protractor. The intersection of the lines is the tip of the angle. This animation illustrates how to use a protractor to measure an angle.Ĭlick and drag the protractor and its blue handles to make some measurements.Ī plan angle defines the space on the plan delimited by two crossing lines.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
